
Close

In today’s world both Nylon 6 and Nylon 6 are widely used synthetics polymer. They have played a vital role in growth and innovation during last few decades. Here we will be examining the properties (similarities and differences) so you can make an informed choice while making a choice between the two.
Introduction to Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 :
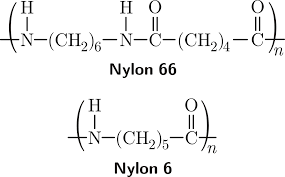
Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 are both polyamides, where the number represents the quantity and type of carbon atoms in the chemical structure.
Nylon 6 is made from caprolactam, which consists of 6 carbon atoms, while nylon 66 is made from adipic acid, which has 6, and hexamethylene diamine, which also has 6.
History of Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 :
In 1930, Du Pont discovered Nylon 66 which was the first synthetics fibre in the world.
In 1939, Paul Schlack discovered Nylon 6.
Both of them due to their very attractive properties were accepted quickly thus becoming the backbone of the synthetics fibre industry.
Technical comparisons of Nylon 6 and 66
Properties of Nylon 6 vs Nylon 66
Both Nylon 6 and 66 are different in many ways but there are many similarities too. Below we have underlined some key core performance characteristics :
Nylon 6 vs Nylon 66: Differences and Comparisons
| NYLON 6 | NYLON 66 |
| Less crystalline | More crystalline |
| Lower mould shrinkage | Exhibits greater mould shrinkage |
| Lower melting point | Higher melting point |
| Lower heat deflection temperature | Higher heat deflection temperature |
| Higher water absorption rate | Lower water absorption rate |
| Poor chemical resistance to acids | Better chemical resistance to acids |
| Withstands high impact and stress and better stands up to hydrocarbons | Better stiffness, tensile modulus and flexural modulus |
| Lustrous surface finish, easy to colour | More difficult to colour |
The most remarkable difference between Nylon 6 and 66 is the mould shrinkage. As Nylon 6 has low mould shrinkage it is more reliable in terms of final part dimensions whereas Nylon 66 higher mould shrinkage makes it skepctical to alteration of dimensions of manufactured goods.
Other notable important differences are their heat deflection value and water absorption rate. Due to higher water absorption and less heat deflection it is less durable in applications where high temperatures are used and more water exposure. In this case Nylon 66 is the preferred choice.
Typical Material Apllications:
Nylon 6:
Nylon 66 :
Final Thoughts :
So after having to know both Nylon 6 and 66 we now know that both have some similar properties but yet due to certain differences the type of application is different. One needs to take into consider processing, aesthetics, appearance and mechanical properties first beforehand.
Nylon 6 has better appearance due to its easy to dye property and lustrous finish. It is preferred mainly in lightweight engineering plastic where high impact and stress is involved. It is the absolute option to go for applications in industries like automotive, industrial and military. As we already know that it is not to be used in applications with high temperatures and expose to water.
Nylon 66 is used in engineering plastic that requires exposure to higher temperatures. Plus the stiffness and good tensile property makes it ideal for applications that required long term performance.